DMZ
What is a DMZ?
DMZ is an abbreviation for “DeMilitarized Zone”, which translates to “demilitarized zone” in Japanese.
See the diagram below.
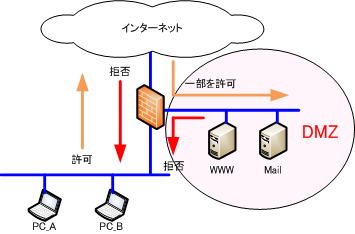
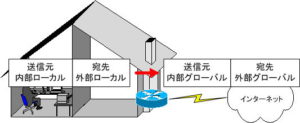
A DMZ is an area in a network connected to the Internet that is isolated from both the Internet side and the internal network side by a firewall.
When translated as “non-armed,” it gives the impression that it is not armed at all, but it is not unarmed. The firewall is configured to allow only necessary traffic to pass through the DMZ and prevent other traffic from passing through the DMZ.
In other words, by placing a server that is open to the public in this DMZ, it is possible to eliminate unauthorized access from the Internet through a firewall.
For example, when placing a WWW server in the DMZ, only packets whose destination IP address is the WWW server and whose source port number is 80 are permitted to flow to the DMZ, and other packets are denied to flow to the DMZ. , can eliminate unauthorized access from the Internet.
If the public server is placed on the internal network instead of the DMZ, even if the public server is hijacked by unauthorized access from the Internet, there will be no damage to the internal network.
By placing the public server in the DMZ, even if the public server is hijacked, the damage will not extend to the internal network.
What I have explained so far is the general meaning of DMZ, but the DMZ function of broadband routers has a slightly different meaning.
DMZ function
The “DMZ function” of broadband routers is used in a slightly different sense from the content explained in “What is DMZ?” above.
The firewall function of the broadband router is set as follows by default.
● Internal network → Internet
・”Allow” communication from the internal network side to the Internet side
● Internet → Internal network
・Return communication from the internal network is “allowed”
・Communication from the Internet side to the internal network is “rejected”
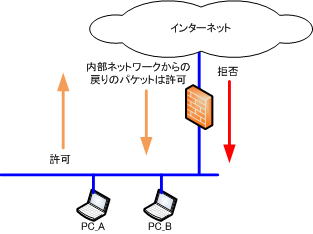
If all communication initiated from the Internet side is rejected, a public server cannot be installed within the internal network.
Therefore, the function to be used is the “DMZ function”.
By using the “DMZ function”, you can transfer all communication from the Internet side to a specific one.
The “DMZ function” of a broadband router is a function that forwards all communications addressed to the global IP address assigned to the Internet side of the broadband router to a single PC assigned a specific private address. .
With the DMZ feature, you can expose a server with a private IP address to the Internet.
However, the “DMZ function” of the broadband router is a very dangerous function. Transferring all communication from the Internet side to a specific one means that the PC designated as DMZ can be attacked from the Internet side as much as you want. In addition, if the server is used as a stepping stone, other PCs located in the internal network will also be exposed to danger.
Therefore, when publishing a server, it is common to use the port forwarding function that will be introduced in the following content. Although the possibility of being used as a stepping stone remains, it is possible to avoid the situation where the Internet side is attacked as much as you want.
*Please note that general providers may prohibit you from setting up a server at home.
If you explain it like this, you may feel that there is not much merit in using the “DMZ function”, but the “DMZ function” is not a function that is used only when setting up a server at home.
By using the “DMZ function” when using applications that use many port numbers, such as network games, or applications that change port numbers dynamically, you will be able to use them normally.
What is port forwarding
The “DMZ function” is a function that forwards all communications addressed to the global IP address assigned to the Internet side of the broadband router to a single PC to which a specific private address is assigned.
This “DMZ feature” is a very dangerous feature. Transferring all communication from the Internet side to a specific one means that the PC designated as DMZ can be attacked from the Internet side as much as you want. In addition, if the server is used as a stepping stone, other PCs located in the internal network will also be exposed to danger.
Therefore, when publishing a server, it is common to use the port forward function. Although the possibility of being used as a stepping stone remains, it is possible to avoid the situation where the Internet side is attacked as much as you want.
Port forwarding is a function to manually set the address translation table (political). By setting this, packets will be sent from the WAN side to a specific destination IP address and destination port number. broadband router forwards the packet to a specific IP address and port number on the LAN side according to the contents of the static address translation table.
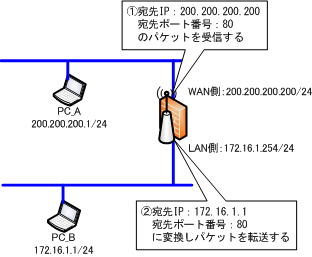
In the figure above, the packets are processed as follows:
(1) Receive packets with destination IP address “200.200.200.200” and destination port number “80”.
(2) Convert the packet to destination IP address “172.16.1.1” and destination port number “80” and transfer the packet.
This port forwarding feature is called differently by different vendors. Also known as “local server”, “virtual (virtual) server” and “static NAT”.