What is SNMP? Manager/Agent
What is SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a protocol for monitoring and managing TCP/IP-based network systems. Recently, the importance of network system management has been recognized, and it is attracting attention.
SNMP has a function to query and manage network traffic and operating status of computers and network devices on the network.
A long time ago, computer systems were networks centered on large machines, but with the downsizing of computers, network systems gradually shifted to systems centered on small machines.
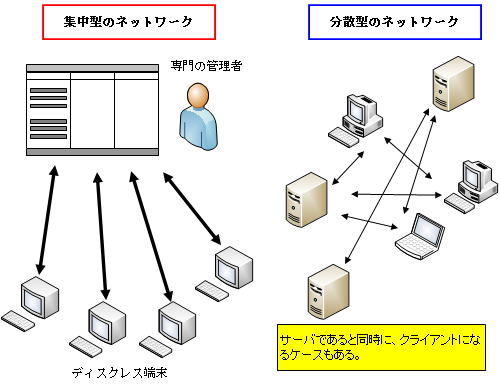
Here comes a serious problem. A centralized network of large machines could be managed with the experience and intuition of a dedicated administrator, but a distributed network is too complex and difficult to manage.
SNMP is being standardized to alleviate this problem.
SNMP Mechanism (Manager/Agent)
SNMP consists of two things:
● agent
● manager
Agents are various devices on the managed side, such as computers, network devices such as routers and switches, and printers, and programs called agents are running on these devices.
This agent manages the parameters that indicate the status of monitored equipment and notifies the status of the equipment in response to requests from the SNMP manager. Agents are always ready to respond to requests from managers.
SNMP has a configuration in which a device to be managed has an agent on standby and is managed by the manager on the monitoring server.
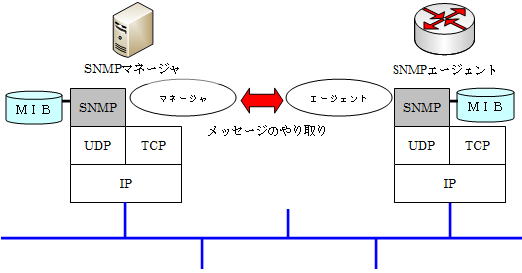
The parameters exchanged between the agent and manager are stored in a database called MIB (Message Information Base) in the monitored device.
The agent extracts information from this MIB and notifies it to the manager, and the manager judges the current status of the device to be monitored from the contents of the received MIB.
SNMP is a protocol positioned above UDP, and uses UDP ports 161 (polling) and 162 (TRAP) to exchange information.