NFS
NFS(Network File System)サービスは、Sun Microsystems社が開発した、ネットワーク上のファイルにアクセスするためのサービスです。NFSサービスは一般的にUDPまたはTCPの2049番ポートが使用されます。
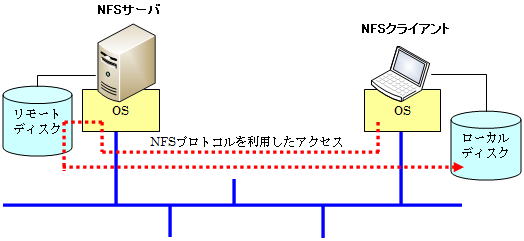
このサービスを利用することで、ネットワーク上の他のコンピュータのファイルシステム(ハードディスクの中身)を、あたかも自分のコンピュータのファイルシステム(ハードディスク)であるかのようにアクセスすることができます。
ネットワーク上のファイルシステムをローカルなファイルシステムと同等に操作することができます。
リモートディスク上のファイルをローカルディスクにあるかのようにアクセスできるという意味で、他のサービスとは比較にならないほど、利用価値の高いネットワークサービスとなっています。
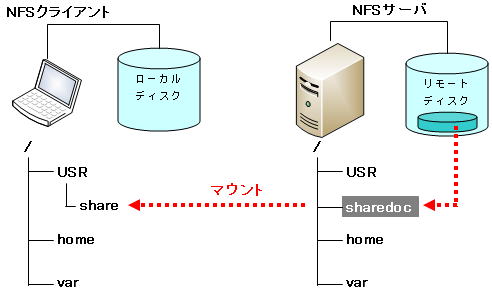
ネットワーク上のディスクにアクセスするには、マウントという作業を行います。マウントする側がNFSクライアント、マウントされる側がNFSサーバと呼びます。
Windowsを中心としたネットワークシステムにおいても、「Microsoft Services for UNIX」を利用することで、WindowsとUNIXが混在する環境においてもファイル共有を実現することができます。
NFSの仕組み
NFSの特徴として、FTPと同様に、Windows、UNIX、MacなどのOSによって異なるファイルシステムの違いを吸収する異機種間接続機能を持っていることが挙げられます。
例えば、UNIXとWindowsでは、ディレクトリを表記する方法が違います。
Windows ・・・ ¥
UNIX ・・・ /
また、UNIX、Macには、ドライブレター(「A:」「B:」)が存在しません。
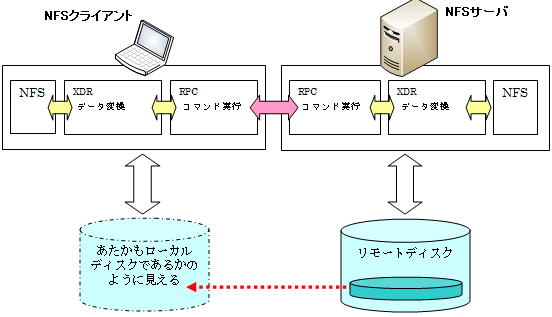
OSのファイルシステムによって、ディレクトリの表現や情報の確認方法など多くの要素が異なります。NFSでは、異なるファイルシステムを共用するために、役割ごとに応じたNFS、XDR(External Data Representation)、 RPC(Remote Procedure Call) などのプロトコルで構成されています。
NFSを構成するプロトコル
| プロトコル | 説明 |
| NFS | ローカルコンピュータとリモートコンピュータとのデータのやり取りをあたかも自分のファイルシステムにアクセスしているかのように見せます。 |
| XDR | OSの違いによって異なるデータ形式を標準形式に変換し、ローカルコンピュータ側で再変換する。異機種間接続のために変換を行う階層です。 |
| RPC | リモートコンピュータに要求を出し、手続きを実行して結果を受け取ります。NFSの最下層で動作します。 |
