What is HSRP?
What is HSRP?
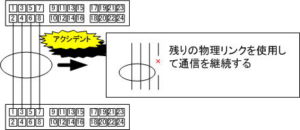
If you lose your default gateway, devices on the segment connected to that default gateway will no longer be able to communicate.
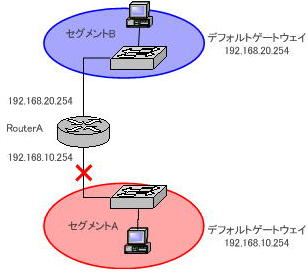
One way to avoid such problems is to create duplicate default gateways.
Suppose you add Router B and reconfigure the network as shown in the diagram below. However, the default gateway of the PC belonging to segment A must be reset to RouterB.
Some OSes allow you to register multiple default gateways, but setting them up on all PCs is a difficult task, and it takes a lot of time to switch, so it’s not practical.
Client PCs usually cannot change their default gateway automatically.
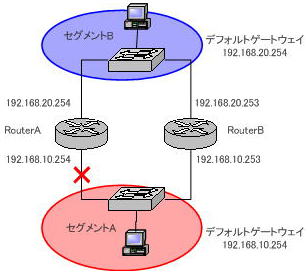
It might seem like it would work if you assigned the same IP address to the two routers, but that would violate the network rule that “duplicate IP addresses must not exist.” , an IP address conflict will occur.
Therefore, the following methods are available for duplicating the default gateway.
・How to use HSRP
・How to use VRRP
Both “HSRP” and “VRRP” are protocols for making default gateways redundant, allowing multiple routers to appear as one router. Router failures can be avoided without changing the PC’s default gateway settings.
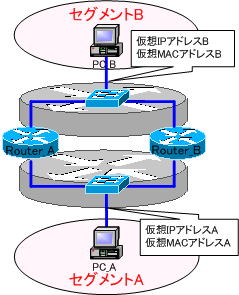
The gray routers above and below are multiple routers disguised as one router. It doesn’t actually exist. Router_A and Router_B share the “virtual IP address” and “virtual MAC address” to pretend to be one router. The router with the higher priority value is the “master”, and the router with the lower priority is the “slave”.
How HSRP works
From here, we will explain how HSRP works.
HSRP and VRRP are both protocols that make default routes redundant and have almost the same functions, but the mechanisms, settings, and detailed operations for achieving redundancy are different.
HSRP is a protocol originally developed by Cisco and is a vendor-specific standard, so it is not compatible with other companies. Several other vendors have developed VRRP to allow for the equivalent of this HSRP.
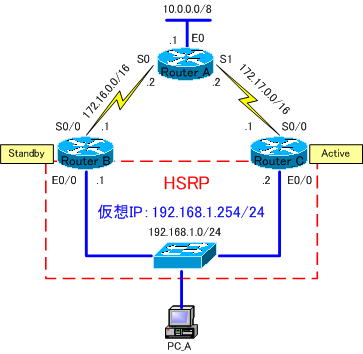
HSRP allows routers in the same group to appear as one router by sharing one “virtual IP address” and “virtual MAC address.” Within the group, one router becomes the Active router and the other routers become Standby routers.
The active router is in charge of routing processing and ARP responses. By default, routers exchange HSRP information by exchanging Hello packets every 3 seconds. This packet uses multicast with UDP port number 1985 and destination IP address “224.0.0.2”.