How email works and how to read email headers
How email works
Here, we will explain the flow from sending to receiving an e-mail.
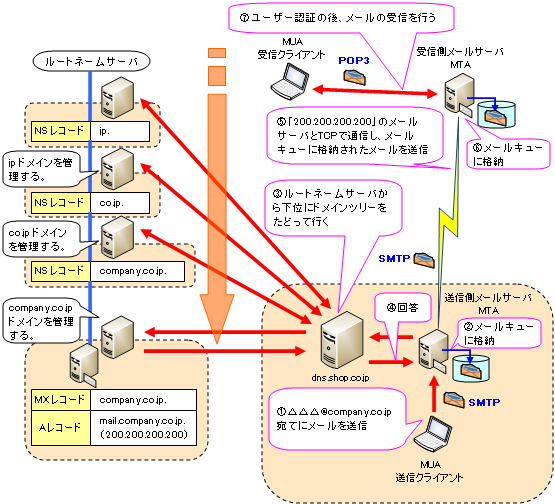
(1) The sending client (MUA) requests the mail server (MTA) to send the mail.
MUA uses TCP port 25 of SMTP protocol with 7-bit ASCII code for text data. Kanji and image files are converted to ASCII code by the BASE64 method.
(2) The mail server requested to send the mail temporarily stores the mail in the mail queue.
(3) The mail server requested to send attempts to resolve the name with the nearest DNS server.
Queries are made in order from the root name server, which is the top of the domain tree.
④Reply the IP address of the destination mail server.
The host name of the destination mail server is also obtained by the MX record, and the corresponding IP address is obtained by the A record.
⑤ After connecting with TCP, send data in the order of source address, destination address, and mail text.
⑥ The mail server at the delivery destination temporarily stores the mail in the mail queue.
(7) After completing user authentication, the MUA of the receiving client receives the mail using TCP port 110 of the POP3 protocol.
There are two methods of user authentication: using the PASS command, which sends the password in plain text, and using the APOP command, which uses a different password each time for user authentication.
How to read email headers
I will explain how to read email headers using spam email as an example.
The spam email example below is from question 1 of afternoon I in the information security exam.

Received reads like this:
Received: from mail server A by mail server B
Received by mail server B from mail server A.
There is no way to disguise the receiving mail server B. from is camouflaged with the Hello command.
Received of the mail server that passed through first comes to the bottom.
emails can be spoofed
E-mail is a medium that can be easily copied or forged.
The flow of email transmission is as follows.
①TCP three-way handshake
②SMTP session
First, start an SMTP session with the HELO or EHLO command.
Then, notify the source and destination with the following command.
Mail command — MAIL From:<reverse-path> (source)
RCPT TO command — RCPT TO:<forward-path> (destination)
By using this command to replace the source and destination with disguised ones, disguised emails can easily be created.
Therefore, various measures are currently being taken.