DHCP (segment identification/message)
DHCP (segment identification)
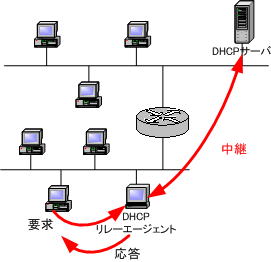
By using the DHCP relay function, you can build a network as shown in the figure below. DHCP servers can be aggregated and managed by a single DHCP server.
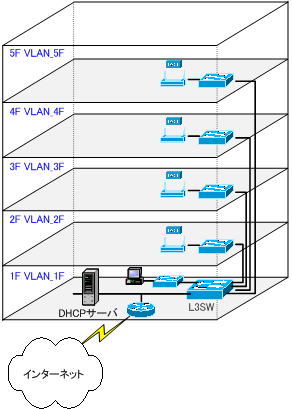
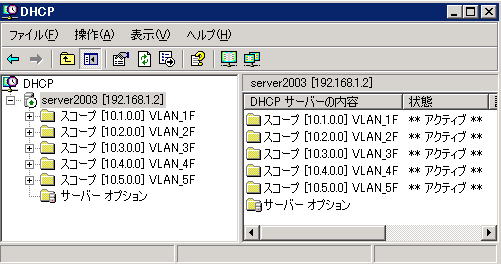
Set a scope for each segment (network) on one DHCP server.
So how does the DHCP server identify segments (networks) and assign different configuration information to each segment?
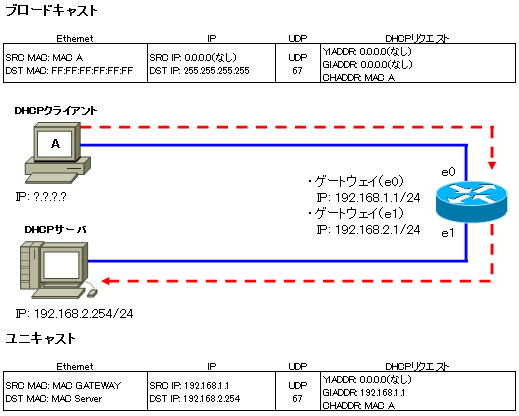
The IP address of “GIADDR” in the DHCP message identifies which subnet the IP address is assigned to and assigns the IP address. If there is no “GIADDR”, it is recognized as the same segment.
● DHCP message format
| information name | explanation |
| CIADDR | Client IP address, used when client is in BOUND, RENEW or REBINDING state. |
| YIADDR | The IP address of the client assigned by the DHCP server (your IP address) |
| SIADDR | DHCP server IP address |
| GIADDR | IP address of the DHCP relay agent. The DHCP server identifies the subnet to which the client belongs by looking at GIADDR. |
| CHADDR | Client’s MAC address |
Before forwarding a packet, store the IP address of the router for that segment in the GIADDR field of the packet. Now when a DHCP client gets that IP address, that address will be the gateway address for the client.
UDP number 67 is used from the client to the DHCP server, and number 68 is used from the DHCP server to the client.
DHCP message format
DHCP is an extension of BOOTP, and the message format etc. are almost the same.
The diagram below shows the DHCP message format.
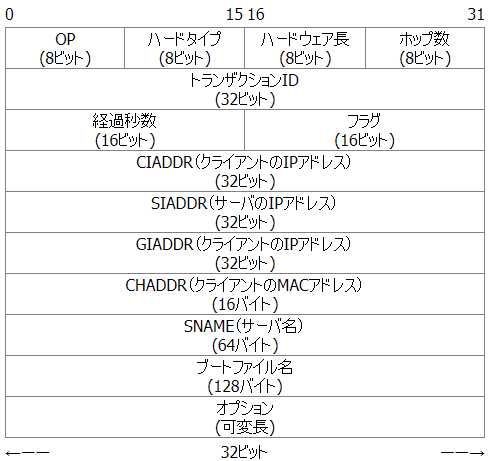
The main items of the DHCP message are shown in the table below.
●Major items of DHCP messages
| information name | explanation |
| CIADDR | Client IP address, used when client is in BOUND, RENEW or REBINDING state. |
| YIADDR | The IP address of the client assigned by the DHCP server (your IP address) |
| SIADDR | DHCP server IP address |
| GIADDR | IP address of the DHCP relay agent. The DHCP server identifies the subnet to which the client belongs by looking at GIADDR. |
| CHADDR | Client’s MAC address |