DHCP (operation, lease renewal and release, command)
DHCP behavior
The flow of DHCP operation is shown in the figure below.
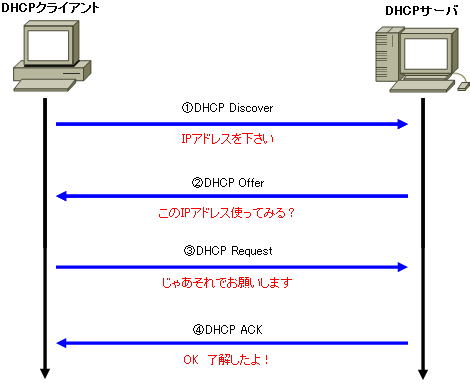
1. DHCP Discover
The client broadcasts “255.255.255.255” and requests to be assigned an IP address.
2. DHCP offers
The DHCP server receives this request and sends a DHCP Offer to the sender asking, “What about this IP address?” At this time, it will be sent to the MAC address of the source client as the destination MAC address.
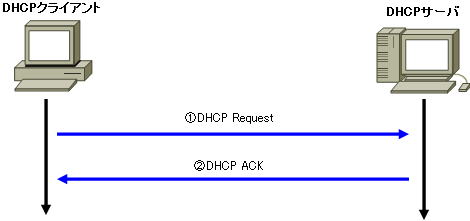
3. DHCP Request
If the client is satisfied with the proposal received in DHCP Offer, it broadcasts a request (DHCP Request) saying “Please let me use that information.”
4. DHCP ACKs
The DHCP server sends an acknowledgment (DHCP ACK) message to the client.
You may be surprised to see this trend. The reason is that the client receives the DHCP Offer and does not configure with that information immediately.
This is because it is assumed that there are multiple DHCP servers. This is so that when there are two or more DHCP Offers for one DHCP Discover, the client can select one and send a DHCP Request.
Also, communication is performed by broadcast between the client and the DHCP server. Therefore, there is a limitation that DHCP cannot be used if there is a DHCP server on the network beyond the router that blocks the broadcast.
*A DHCP relay agent is required to access the DHCP server beyond the router. This feature is usually supported by routers.
Renewal and Release of Leases
The assignment of IP addresses by DHCP servers to DHCP clients is called a lease.
This leased IP address is allowed to be used only within the lease period defined by the DHCP server. A DHCP client cannot use an IP address beyond the lease time.
Therefore, if the DHCP client wants to use the IP address beyond the lease period, it will request renewal of the lease period.
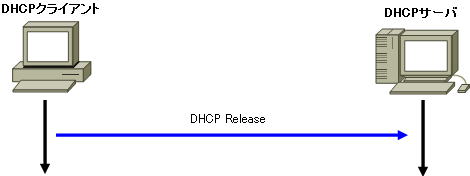
Also, when the DHCP client no longer needs an IP address, such as when the power is turned off, DHCP Release is performed as shown in the figure below.
In the case of Windows, when half of the lease period has passed, the DHCP server that has leased the IP address is requested to renew the lease period. If this renewal succeeds, the lease will be extended.
If the DHCP server fails to renew due to reasons such as being down, the DHCP client will further ask another DHCP server to lease the IP address when 87.5% of the lease expiration has passed. , broadcast a DHCP Request.
If no DHCP server receives permission to renew, the lease expires and the DHCP client stops using the IP address.
Commands to do DHCP lease/release
If you are automatically obtaining an IP address by DHCP, you can manually release (Release) and renew (Renew) the IP address obtained from DHCP.
Regarding automatic acquisition of release (Release) and update (Renew), it is automatically performed when the PC starts up, but if you want to check the operation of the DHCP server immediately after the automatic acquisition fails , it is convenient to update with the command
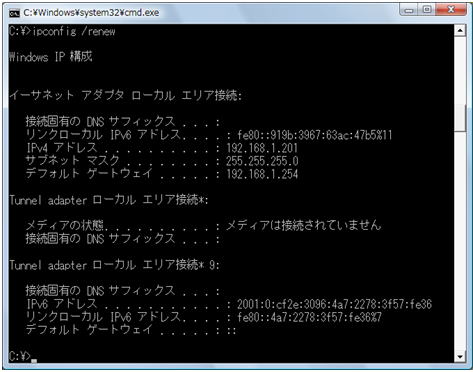
Use the “ipconfig command” to release and update manually. This command is a command to display the setting information related to TCP/IP on the command prompt. You can get a simple display with “ipconfig” and get detailed information with “ipconfig /all”.
This “ipconfig command” can manually release and renew DHCP by specifying options.
ipconfig /release command
Releases the IP address leased from the DHCP server for the specified network adapter. If the adapter name is omitted, all adapters are targeted.
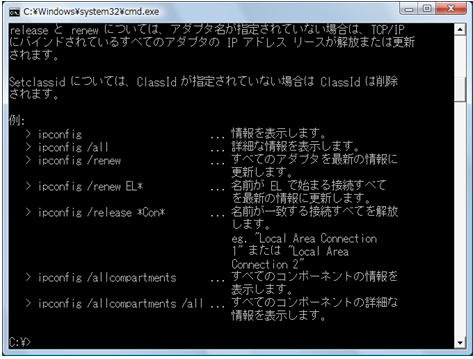
ipconfig /renew command
The IP address will be released (0.0.0.0), and the IP address will be obtained automatically again. If the adapter name is omitted, all adapters are targeted.